How does a meniscus tear occur?
The knee joint is the most frequently injured area in the human body and the most common cause of surgery is meniscus tears. Contrary to popular belief, meniscus is a health problem that can occur not only in athletes but also in every part of society and at any age.
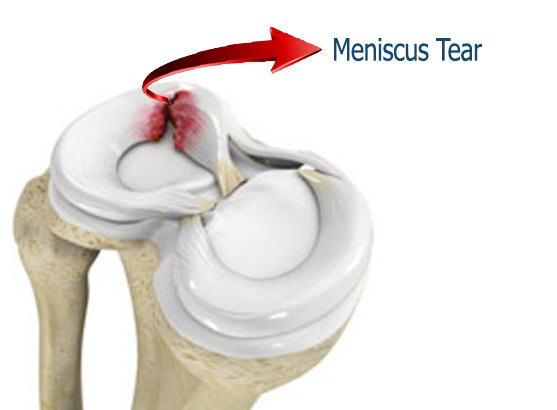
Meniscus tears develop as a result of serious difficulties such as sports trauma and traffic accidents. As a result of rotation on the fixed foot, the meniscus is torn between the knee bones and rupture.
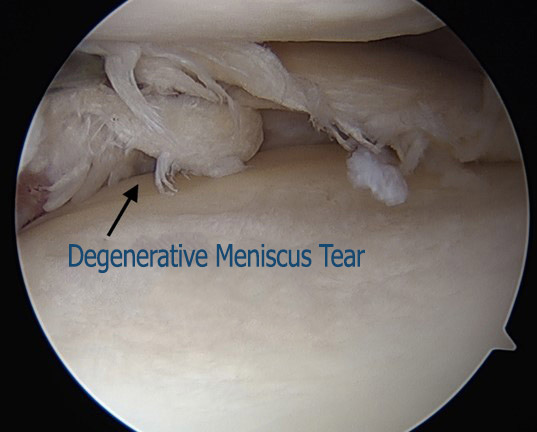
In the elderly, the already worn meniscus can be torn as a result of small movements.
In children, congenital abnormalities of the meniscus (such as discoid meniscus) may pave the way for early tears.
What are the signs of meniscus tear?
Meniscus rupture by force in youth causes to; pain, stinging or tearing sensation in the patient’s knee. Intra-knee haemorrhage may occur due to meniscus tear, in this situation swelling is occurred on the knee. In a period of about one month, all complaints are relieved and only the punctual tenderness remains in the torn area. If the torn meniscus stucks under the knee, the knee will lock. In this case, the patient cannot open or close its knee. If the knee is forced to move, sometimes the knee movements can become available with the feeling of jumping. In both cases, the tear is large and requires immediate surgery.
Ruptures in elderly patients cause milder complaints. Pain is not unbearable if cartilage wear has not occurred. Occasionally there is a feeling of stuck, but locking is rare. Swelling may occur due to fluid increase in the joint.
In children with discoid meniscus, a feeling of jumping is seen in the knee. When a rupture occurs pain increases, entanglement and locking may occur.
How is meniscus rupture diagnosed?
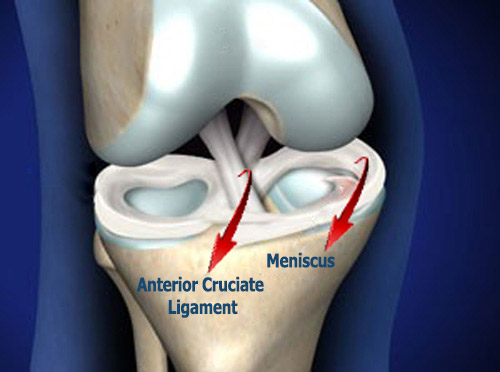
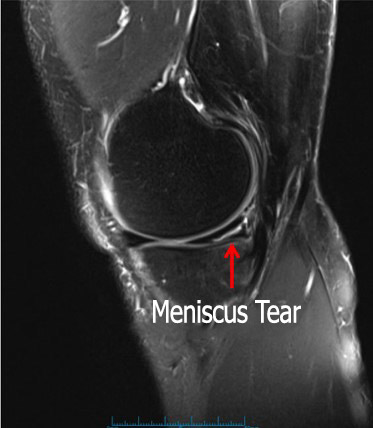
Diagnosis of meniscus rupture is made by the mechanism of event, complaints of the patient and knee examination. The location, shape and size of the meniscus tear can be determined with an accuracy of 95% by MRI. In addition, cartilage, anterior cruciate ligament and lateral ligament injuries associated with meniscus tear can be detected on knee MRI. It is possible to diagnose meniscus tears by arthroscopic examination which cannot be detected despite all examinations.