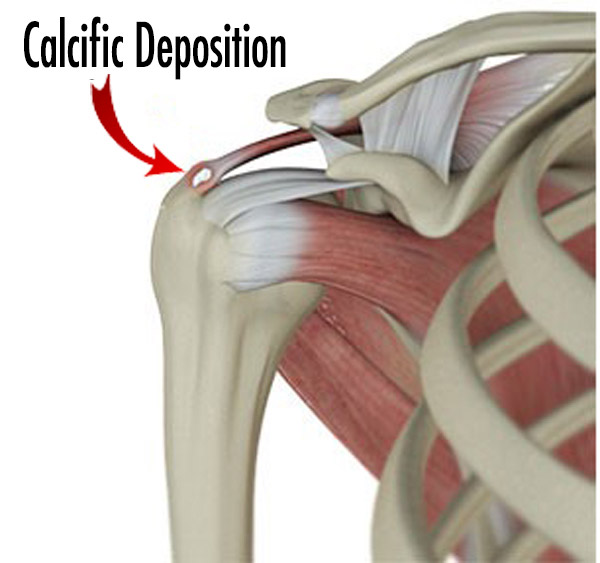
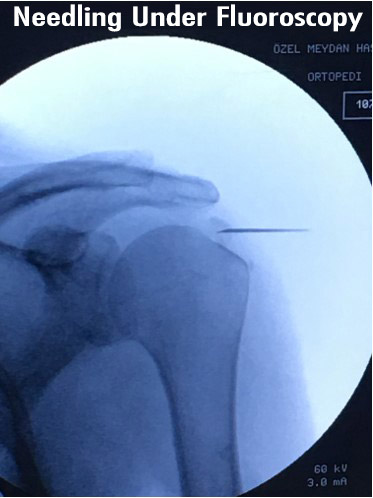
Calcific tendonitis is one of the most painful diseases of the shoulder. Causes unbearable pain in the shoulder. Shoulder calcific tendinitis is a disease characterized by the accumulation of calcium in the tendons of the rotating muscles of the shoulder. The exact cause of calcific tendinitis is unknown. It is a more common disease between the ages of 40-60 and especially in women. It is known that diabetes increases the being in tendency to it. There is no other known serious risk factor.
What are the signs of Calcific Tendinitis?
The biggest complaint of the patients is severe pain. Patients complain of severe pain in the shoulder, especially at night, in the acute (early) period. Lifting the arm to the side or even moving it a little bit is very painful. Patients usually hold their arms attached to their body and immobilized. This period lasts an average of two weeks. In chronic period, weakening of muscles around the shoulder develops due to ongoing pain and inactivity.