What is Arthroscopic Surgery (Closed Surgery)?
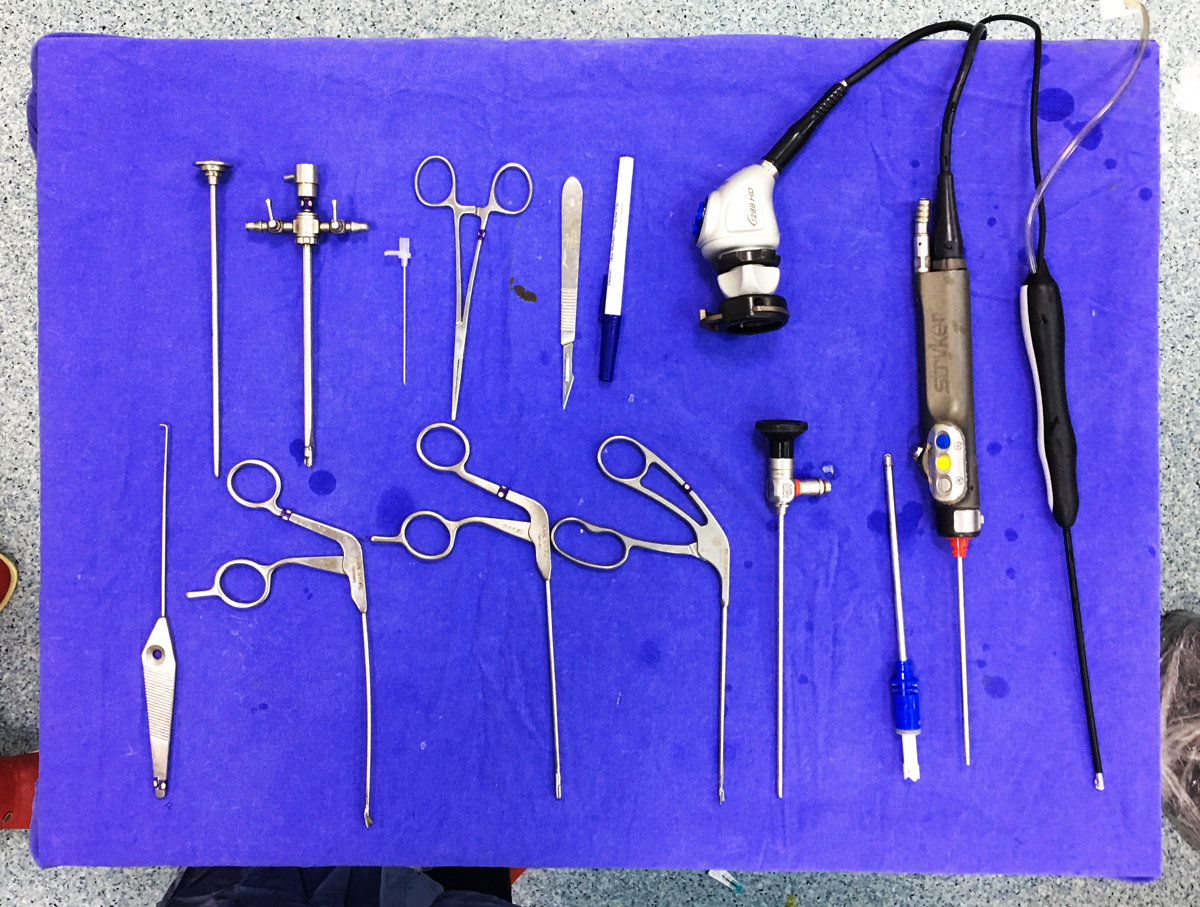
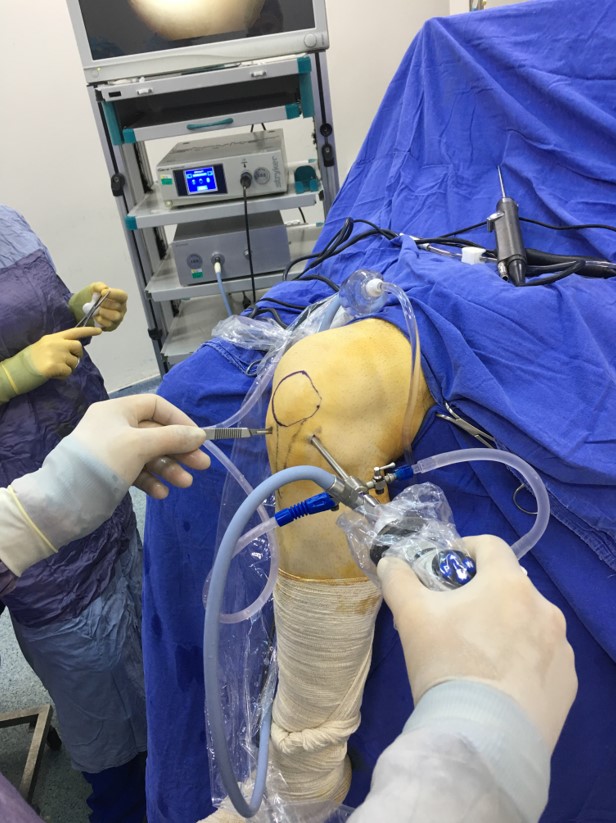
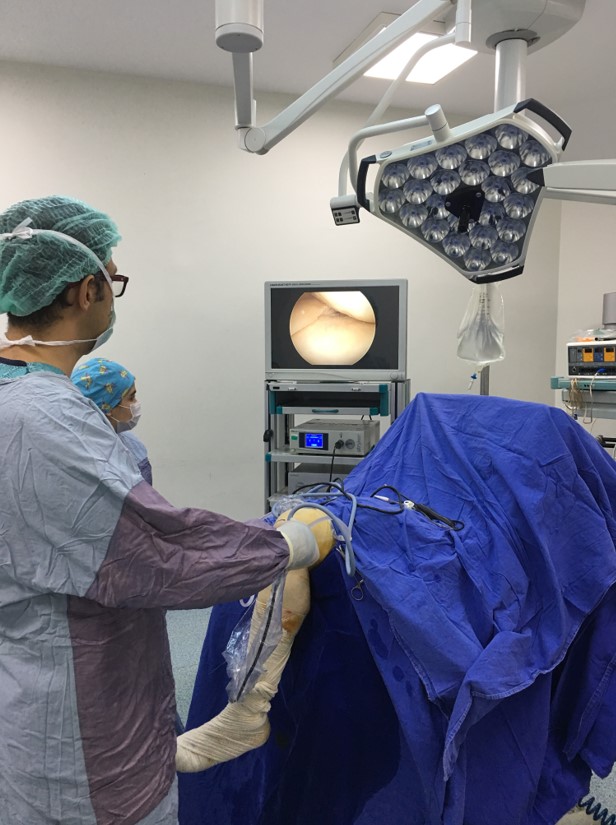
Arthroscopic surgery is the visualization of the joint with an imaging device called arthroscopy, examination of the joint inside with various instruments and performing the necessary surgical procedure, by entering to joints through small holes which are opened in the skin.